1.1 Correlating with UUIDs
SData uses Universally Unique Identifiers (UUIDs) to correlate resources across applications.
If the same resource exists in several applications, it is likely to have different ids in different applications. For example, if contact “John Doe” exists in a CRM and an ERP application, it may have an id of 537 in the CRM application and an id of C0018 in the ERP application. As this example shows, the ids may even have a different structure, they may be numeric on one side and alphanumeric on the other side. These ids are called “local ids”.
Processes like synchronization or cross application reporting require that resources representing the same object in different applications be correlated with each other. SData recommends that the correlations be established with a UUID: every application maintains a mapping between local ids and UUIDs for all the resources that are correlated and the fact that two resources from different applications share the same UUID indicates that they are correlated with each other.
The following diagram illustrates this with three resources that are correlated thanks to a common UUID:
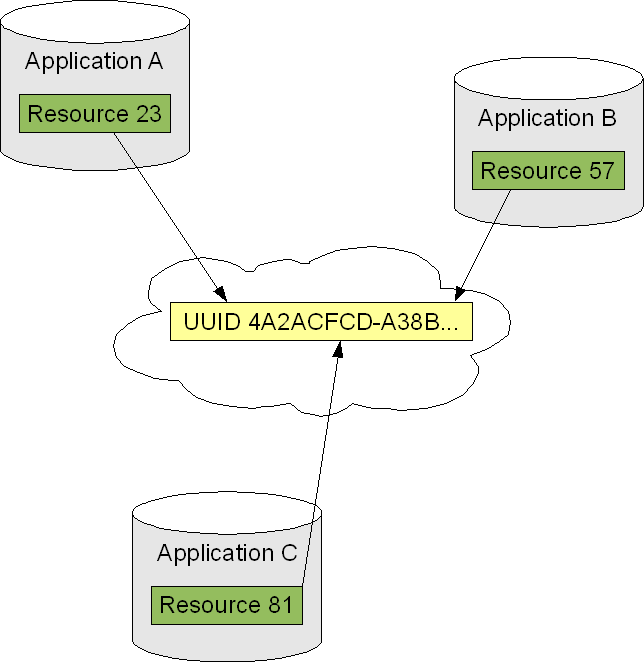
This approach is a distributed approach. Each application maintains one half of the complete mapping and does not need to be aware of the local ids of other applications. This approach does not require any central repository where local ids from different applications would be correlated with each other. This distributed nature has important impacts on overall manageability and also on performance (correlations can be resolved locally, without requiring roundtrips to a repository).
It is important that the UUIDs be generated by a true UUID generator. They should not be crafted to encode one or more local ids because this would go against the distributed nature of the approach and it would also introduce a risk of collisions (local ids may collide across tables).
If an application uses UUIDs internally as primary keys in its tables, it should not reuse these UUIDs for linking. Instead, it should maintain a separate UUID for linking. This is required to conform to the allocation policy discussed in the following wiki sections.
A provider participating in cross-application linking MUST expose a UUID as an external identifier for linked resources. The relationship between the UUID and the resource is one-to-one and onto. The provider SHOULD avoid usage of the external UUIDs within the application itself.


